itkImageFileReader¶
-
MLModule¶ genre ITKToolsauthor Wolf Spindlerpackage FMEwork/ReleaseMeVisdll MLITKManualBindingdefinition MLITKManualBinding.def see also ImageLoad,ImageSave,itkImageFileWriter,MLImageFormatSave,MLImageFormatFileCache,MLImageFormatLoad,FieldContainerViewkeywords load,image,read,import,file,import,nifti,nrrd,bmp,nii,pic,mha,mhd,tiff,vtk,spr,lsm,jpg,jpeg,gipl,img,hdr,imggz,mask,jpeg2000
Purpose¶
The itkImageFileReader module modules permits access to many (not all) file formats supported in itk.
Be aware that itkImageFileReader therefore has several backends with different behaviors and also numerous limitations, do not expect that all stored image information is completely loaded. For known limitations see the section about known issues in Tips of itkImageFileWriter.
Some additional known reader issues are
- Handling of unicodes does not work for .nrrd format on windows, i.e. files containing e.g. umlauts may not be readable. Workaround: rename the file and try again.
- Loaded .lsm files in first runs after start log the error “Function unknown: Message ITK ERROR: LSMImageIO(0000027DE9546AB0): Tag cannot be found: Handling ITK ERROR: LSMImageIO(0000027DE9546AB0): Tag cannot be found Loaded data may be undefined”. The origin of this error is still unknown or whether it still relevant in subsequent usages.
- Only a few file formats honor the information of image origins at all: Currently known are .hdr/.img, .nrrd, and .mhd/.raw. All other formats do not store them at all. If you have written data with corrected subvoxel shifts (or not), you may not or may want to correct this when loading the data to get the same MeVisLab world coordinates afterwards. If
Correct Sub Voxel Shiftis used on file formats which do not support image origins then always (0,0,0) is used as origin before correction. Be sure to have tested the combination for you specific file format before relying on it. - In order to remove ambiguities in coordinate system handling, in the past a few changes have been applied in itk/vtk, thus files written with very old versions of itk/vtk may not have the same orientation any as they on time of saving. See Force Direction Cosine Write in
itkImageFileWriterfor details.
Usage¶
Set Dimension field with the dimension of the file to be loaded, the voxel type for the output image to be created in Voxel Type field and then then use the Browse button to select the file to be loaded. See Tips for loading color images.
Tips¶
- Use
itkImageFileReaderfor itk example data. - Use ImageLoad for MeVisLab example data.
- File loading maps the entire image in memory. For large images this can lead to out of memory problems.
- Color images can only be read correctly if color channels are stored in separate image planes (r,r,r,….g,g,g,…b,b,b). If color channels are stored interleaved (r,g,b,….r,g,b,…r,g,b)the images can be read into 3d integer vector voxels and then converted to a color image with the module TypeToScalars using Output Dimension C. See
Voxel Typefor available types. Note that 8 bit integer vectors are not useful for many RGB images, because they use signed integers with ranges from -128 to 127 and RGB values often exceed the ranges. 16 bit signed integer vector with three components are the best matching type. - The
itkImageFileReaderreads tiff file written with MeVisLab only as 2d and in 8 bit without paging which leads to limited data quality and dimension when loading MeVisLab example data which are stored in that format. Use the ImageLoad module for full 3D paged tiff files of any data type.
Output Fields¶
The loaded file is available at output 0. On load failures the output normally will be deactivated. Check the status message in the Info field or in the image output tool tip for additional information.
outputMetaData¶
-
name:outputMetaData, type:MLBase¶ This is an output connector for a FieldContainer which is filled with the meta data information which is loaded when an image is opened. Many images or file loaders do not provide such meta data and in this case the output FieldContainer is empty; otherwise it can be displayed easily with a
FieldContainerViewmodule.
Parameter Fields¶
Field Index¶
Auto: Bool |
Loader Type: String |
Close: Trigger |
Meta Data: String |
Component Type: String |
Num Dimensions: Integer |
Correct Sub Voxel Shift: Bool |
Open: Trigger |
Dimension: Enum |
Pixel Type: String |
File Name: String |
suppressErrorPosting: Bool |
File Type: String |
True File Name: String |
Info: String |
Voxel Type: Enum |
The following parameters are available in the module panel:
Visible Fields¶
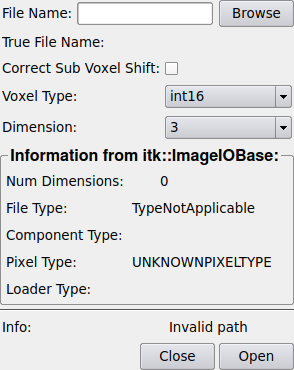
True File Name¶
-
name:fileName, type:String, persistent:no¶ This read-only field shows the real file name used to save the file. It a a resolved version of the File Name field which might contains variables.
Default is “”.
Voxel Type¶
-
name:fileDataType, type:Enum, default:int16¶ This is the voxel type to be used for the loaded file. Note that files could be stored in another voxel type - then the voxel type is automatically cast to the selected one. If a file cannot be loaded because the voxel components cannot be converted then try other voxel types which are larger or may fit better to the stored voxel type. Compiled are the following types:
- Scalar types: 8,16, 32, and 64 bit signed and unsigned integers, float, double
- Matrix types: 3x3, 4x4, 5x5, 6x6 float and double
- Floating point vectors: 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 16, 32 float and double
- Quaternions: float and double
- Complex: float and double
- Vectors with 8 or 16 bit signed integers: with 2, 3, 4 components
- Vectors with 32 bit signed integers: with 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 16, and 32 components.
Values:
| Title | Name |
|---|---|
| int8 | int8 |
| unsigned int8 | unsigned int8 |
| int16 | int16 |
| unsigned int16 | unsigned int16 |
| int32 | int32 |
| unsigned int32 | unsigned int32 |
| float | float |
| double | double |
| int64 | int64 |
| unsigned int64 | unsigned int64 |
| complexf | complexf |
| complexd | complexd |
| quaternionf | quaternionf |
| quaterniond | quaterniond |
| vecf2 | vecf2 |
| vec2 | vec2 |
| vecf3 | vecf3 |
| vec3 | vec3 |
| vecf4 | vecf4 |
| vec4 | vec4 |
| vecf5 | vecf5 |
| vec5 | vec5 |
| vecf6 | vecf6 |
| vec6 | vec6 |
| vecf7 | vecf7 |
| vec7 | vec7 |
| vecf8 | vecf8 |
| vec8 | vec8 |
| vecf9 | vecf9 |
| vec9 | vec9 |
| vecf10 | vecf10 |
| vec10 | vec10 |
| vecf16 | vecf16 |
| vec16 | vec16 |
| vecf32 | vecf32 |
| vec32 | vec32 |
| vecf64 | vecf64 |
| vec64 | vec64 |
| matf2 | matf2 |
| mat2 | mat2 |
| matf3 | matf3 |
| mat3 | mat3 |
| matf4 | matf4 |
| mat4 | mat4 |
| matf5 | matf5 |
| mat5 | mat5 |
| matf6 | matf6 |
| mat6 | mat6 |
| Vector2i8 | Vector2i8 |
| Vector2i16 | Vector2i16 |
| Vector2i32 | Vector2i32 |
| Vector2i64 | Vector2i64 |
| Vector3i8 | Vector3i8 |
| Vector3i16 | Vector3i16 |
| Vector3i32 | Vector3i32 |
| Vector3i64 | Vector3i64 |
| Vector4i8 | Vector4i8 |
| Vector4i16 | Vector4i16 |
| Vector4i32 | Vector4i32 |
| Vector4i64 | Vector4i64 |
| Vector5i8 | Vector5i8 |
| Vector5i16 | Vector5i16 |
| Vector5i32 | Vector5i32 |
| Vector5i64 | Vector5i64 |
| Vector6i8 | Vector6i8 |
| Vector6i16 | Vector6i16 |
| Vector6i32 | Vector6i32 |
| Vector6i64 | Vector6i64 |
| Vector7i8 | Vector7i8 |
| Vector7i16 | Vector7i16 |
| Vector7i32 | Vector7i32 |
| Vector7i64 | Vector7i64 |
| Vector8i8 | Vector8i8 |
| Vector8i16 | Vector8i16 |
| Vector8i32 | Vector8i32 |
| Vector8i64 | Vector8i64 |
| Vector9i8 | Vector9i8 |
| Vector9i16 | Vector9i16 |
| Vector9i32 | Vector9i32 |
| Vector9i64 | Vector9i64 |
| Vector10i8 | Vector10i8 |
| Vector10i16 | Vector10i16 |
| Vector10i32 | Vector10i32 |
| Vector10i64 | Vector10i64 |
| Vector16i8 | Vector16i8 |
| Vector16i16 | Vector16i16 |
| Vector16i32 | Vector16i32 |
| Vector16i64 | Vector16i64 |
| Vector32i8 | Vector32i8 |
| Vector32i16 | Vector32i16 |
| Vector32i32 | Vector32i32 |
| Vector32i64 | Vector32i64 |
| Vector64i8 | Vector64i8 |
| Vector64i16 | Vector64i16 |
| Vector64i32 | Vector64i32 |
| Vector64i64 | Vector64i64 |
Auto¶
-
name:autoDetermineDataType, type:Bool, default:FALSE¶ If enabled then the reader tries to select the voxel type of the file automatically (might be more expensive in a few cases), otherwise the manually selected one is used. Note that automatic type detection might not work in all situations (for example if a reader does not support unsigned char voxel type which is needed for testing).
Correct Sub Voxel Shift¶
-
name:correctSubVoxelShift, type:Bool, default:TRUE¶ ITK and ML use different origins for voxel coordinates (at center or atorigin of the pixel). This is usually corrected on transfers of image data between itk and ML algorithms, however, when loading images this is sometimes not expected, because e.g. an image origin at (0,0,0) is desired. Therefore this correction is disabled by default when loading images. If the correction is wanted then this flag shall can be activated.
Dimension¶
-
name:fileDimension, type:Enum, default:3¶ When loading data the created output file will have this dimension. If the stored file has a higher dimension, only an image of the specified dimension will be generated. If a file cannot be loaded because the image dimension cannot be converted then try other dimensions.
Values:
| Title | Name |
|---|---|
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 4 |
| 6 | 6 |
Info¶
-
name:info, type:String, default:Invalid path¶ This is a read-only status field showing information and error information, normally about the recent load operation.
Close¶
-
name:close, type:Trigger¶ Closes a file if it is open. This can be useful to remove file locks, when a file is overwritten by another file.
Open¶
-
name:open, type:Trigger¶ This opens or reopens a file. Normally this is done automatically when specifying any load parameter, however, changes of the file on disk do not lead to a file reopen. This can be done manually using this button.
Num Dimensions¶
-
name:numDims, type:Integer, default:0¶ Dimensionality as it was found in the file by itk::ImageIOBase.
File Type¶
-
name:fileType, type:String, default:TypeNotApplicable¶ File type as it was found in the file by itk::ImageIOBase (normally ASCII or Binary).
Component Type¶
-
name:componentType, type:String¶ Scalar component type as it was found in the file by itk::ImageIOBase.
Pixel Type¶
-
name:pixelType, type:String, default:UNKNOWNPIXELTYPE¶ The way pixels are composed as it was found in the file by the itk::ImageIOBase.
Meta Data¶
-
name:outputMetaDataStr, type:String¶ This is a textual output for the FieldContainer which is filled with the meta data information loaded while an image is opened. This information is also passed to the base output connector. Many images or file loaders do not provide such meta data and in this case this text field is empty. A
FieldContainerViewmodule provides additional features to filter elements of such a loaded meta data container.
File Name¶
-
name:unresolvedFileName, type:String, deprecated name:path¶ This is the file name parameter which normally should contain the full absolute path to the file to be loaded. Note that also variables can be used such as $(NETWORK), $(HOME), and $(DemoDataPath)to specify paths into the current network directory, the user’s home direcory and to the installed example data directory of MeVisLab.
Default is “”.