itkImageFileWriter¶
-
MLModule¶ genre ITKToolsauthor Wolf Spindlerpackage FMEwork/ReleaseMeVisdll MLITKManualBindingdefinition MLITKManualBinding.def see also ImageLoad,ImageSave,itkImageFileReader,MLImageFormatSave,MLImageFormatFileCache,MLImageFormatLoadkeywords write,save,store,export,IO,ITK,Meta,image,files,export,nifti,nrrd,bmp,nii,pic,mha,mhd,tiff,vtk,spr,lsm,jpg,jpeg,gipl,img,hdr,imggz,mask
Purpose¶
The itkImageFileWriter is a wrapper module for the itk meta file IO writer. It can save many - not all - ML image configurations with a number of file formats. Be aware that itkImageFileWriter has several backends with several different behaviors and also several limitations, do not expect that all image information is completely stored and/or reloaded. For known limitations see the section about known issues in Tips.
For example the following file formats are supported:
- Analyze: .img, .hdr, .img.gz
- BioRad: .pic
- Bitmap: .bmp
- Dicom: .dcm, .dicom
- Gipl: .gipl
- JPEG: .jpg, .jpeg
- Laser Scan Microscopy: .lsm
- MetaImage: .mha .mhd
- Nearly Raw Raster Data: .nrrd
- Nifti: .nii
- PNG: .png
- Stimulate: .spr
- Tiff: .tif, .tiff
- VTK: .vtk
The file format to be used to write the file is determined by the file extension used in the File Name field.
Usage¶
Set up a file name in the File Name field, use an appropriate file extension and press save.
Tips¶
The following issues are known:
- Saving color images is still not supported, because internal data layouts of itk and ML differ for color images. Consider writing images with vector voxels instead and decompose them after reading to color images again. Note, however, that this is not straightforward for different file formats, color models, and voxel types. See also Tips in
itkImageFileReader. - The
itkImageFileWriterloads the entire input image into memory before it can save the image, because paging is currently not supported. For large image files this can lead to out of memory problems. - The
itkImageFileWriterdoes not save additional image information such as DICOM tags, ML image properties and so on, even if formats such as DICOM are written. Properties like the image coordinate system and the voxel size are stored if the file format supports it, however see Force Direction Cosine Write for limitations. - For problems with saving the image coordinate system see
Force Direction Cosine Write. - Many saved file formats do not support image compression. In this case the
Use Compressionflag is ignored. - Many saved file formats do not support an image origin in world coordinates, see
Correct Sub Voxel Shiftfor details, also corresponding notes initkImageFileReader. - Not all voxel types and image dimensions are supported and many file formats as well cannot save many voxel types or file dimensions. Normally (not always) the writer will show error information in the
Infofield then. - Some formats store images in lossy formats. Stored and reloaded images therefore may have different contents though.
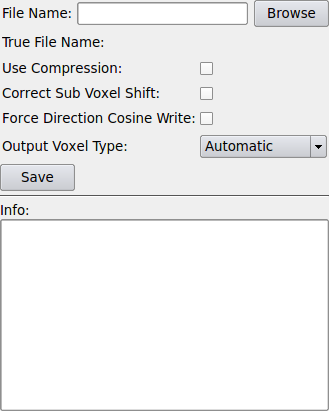
Input Fields¶
At this input the image file to be saved must be connected before saving the file.
Parameter Fields¶
Field Index¶
Correct Sub Voxel Shift: Bool |
File Name: String |
Force Direction Cosine Write: Bool |
Info: String |
Output Voxel Type: Enum |
Save: Trigger |
True File Name: String |
Use Compression: Bool |
Visible Fields¶
True File Name¶
-
name:fileName, type:String, persistent:no¶ This read-only field shows the real file name used to save the file. It a a resolved version of the File Name field which might contains variables.
Use Compression¶
-
name:useCompression, type:Bool, default:FALSE¶ If this flag is enabled and Save is pressed the stored file is compressed if the used file format supports a compressor. In all other cases this flag is normally ignored.
Correct Sub Voxel Shift¶
-
name:correctSubVoxelShift, type:Bool, default:TRUE¶ ITK and ML use different origins for voxel coordinates (at center or at origin of the pixel). This is usually corrected on image data between itk and ML algorithms, however, when saving images this is sometimes not expected, because e.g. an image origin at (0,0,0) is desired. Therefore this correction is disabled by default when writing images. If the correction is wanted then this flag shall can be activated.
Notes and known issues:
- Only a few file formats honor the information of image origins at all: Currently known are .hdr/.img, .nrrd, and .mhd/.raw. All other formats do not save them at all.
- If you write data with corrected subvoxel shifts (or not), you may not or may want to correct this when loading the data to get the same MeVisLab world coordinates afterwards.
Force Direction Cosine Write¶
-
name:forceDirectionCosineWrite, type:Bool, default:FALSE¶ If there are non scale and non translational values in the ML world matrix the written direction cosine matrix will be a non id matrix. As far as it is known currently, this is not handled consistently by itk file IO classes, because there is some inconsistent handling in them. Therefore this writer suppresses writing of such files if it is not explicitly enabled by this flag. See the following links for further information:
http://www.itk.org/Bug/view.php?id=6558
http://www.itk.org/Wiki/ITK_Release_4.0_Orientation_by_Michael
http://www.itk.org/Wiki/ITK_Release_4.0_Orientation_by_Torsten
http://www.itk.org/Wiki/ITK_Release_4.0_Orientation_by_Kent
http://www.itk.org/pipermail/insight-users/2008-November/027797.html
http://www.itk.org/pipermail/insight-users/2008-November/027882.html
http://www.nabble.com/itk::Image-vs.-itk::OrientedImage-td19899159.html
Output Voxel Type¶
-
name:outputVoxelType, type:Enum, default:Automatic¶ Input voxels are cast to this selected and written output type (even if it causes information loss). The default mode Automatic directly writes the input voxel data without type cast, which is the recommended mode. Note that many writers do not support many voxel formats. Compiled are the following types:
- Scalar types: 8,16, 32, and 64 bit signed and unsigned integers, float, double
- Matrix types: 3x3, 4x4, 5x5, 6x6 float and double
- Floating point vectors: 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 16, 32 float and double
- Quaternions: float and double
- Complex: float and double
- Vectors with 8 or 16 bit signed integers: with 2, 3, 4 components
- Vectors with 32 bit signed integers: with 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 16, and 32 components.
Values:
| Title | Name |
|---|---|
| Automatic | Automatic |
| int8 | int8 |
| unsigned int8 | unsigned int8 |
| int16 | int16 |
| unsigned int16 | unsigned int16 |
| int32 | int32 |
| unsigned int32 | unsigned int32 |
| float | float |
| double | double |
| int64 | int64 |
| unsigned int64 | unsigned int64 |
| complexf | complexf |
| complexd | complexd |
| quaternionf | quaternionf |
| quaterniond | quaterniond |
| vecf2 | vecf2 |
| vec2 | vec2 |
| vecf3 | vecf3 |
| vec3 | vec3 |
| vecf4 | vecf4 |
| vec4 | vec4 |
| vecf5 | vecf5 |
| vec5 | vec5 |
| vecf6 | vecf6 |
| vec6 | vec6 |
| vecf7 | vecf7 |
| vec7 | vec7 |
| vecf8 | vecf8 |
| vec8 | vec8 |
| vecf9 | vecf9 |
| vec9 | vec9 |
| vecf10 | vecf10 |
| vec10 | vec10 |
| vecf16 | vecf16 |
| vec16 | vec16 |
| vecf32 | vecf32 |
| vec32 | vec32 |
| vecf64 | vecf64 |
| vec64 | vec64 |
| matf2 | matf2 |
| mat2 | mat2 |
| matf3 | matf3 |
| mat3 | mat3 |
| matf4 | matf4 |
| mat4 | mat4 |
| matf5 | matf5 |
| mat5 | mat5 |
| matf6 | matf6 |
| mat6 | mat6 |
| Vector2i8 | Vector2i8 |
| Vector2i16 | Vector2i16 |
| Vector2i32 | Vector2i32 |
| Vector2i64 | Vector2i64 |
| Vector3i8 | Vector3i8 |
| Vector3i16 | Vector3i16 |
| Vector3i32 | Vector3i32 |
| Vector3i64 | Vector3i64 |
| Vector4i8 | Vector4i8 |
| Vector4i16 | Vector4i16 |
| Vector4i32 | Vector4i32 |
| Vector4i64 | Vector4i64 |
| Vector5i8 | Vector5i8 |
| Vector5i16 | Vector5i16 |
| Vector5i32 | Vector5i32 |
| Vector5i64 | Vector5i64 |
| Vector6i8 | Vector6i8 |
| Vector6i16 | Vector6i16 |
| Vector6i32 | Vector6i32 |
| Vector6i64 | Vector6i64 |
| Vector7i8 | Vector7i8 |
| Vector7i16 | Vector7i16 |
| Vector7i32 | Vector7i32 |
| Vector7i64 | Vector7i64 |
| Vector8i8 | Vector8i8 |
| Vector8i16 | Vector8i16 |
| Vector8i32 | Vector8i32 |
| Vector8i64 | Vector8i64 |
| Vector9i8 | Vector9i8 |
| Vector9i16 | Vector9i16 |
| Vector9i32 | Vector9i32 |
| Vector9i64 | Vector9i64 |
| Vector10i8 | Vector10i8 |
| Vector10i16 | Vector10i16 |
| Vector10i32 | Vector10i32 |
| Vector10i64 | Vector10i64 |
| Vector16i8 | Vector16i8 |
| Vector16i16 | Vector16i16 |
| Vector16i32 | Vector16i32 |
| Vector16i64 | Vector16i64 |
| Vector32i8 | Vector32i8 |
| Vector32i16 | Vector32i16 |
| Vector32i32 | Vector32i32 |
| Vector32i64 | Vector32i64 |
| Vector64i8 | Vector64i8 |
| Vector64i16 | Vector64i16 |
| Vector64i32 | Vector64i32 |
| Vector64i64 | Vector64i64 |
Save¶
-
name:save, type:Trigger¶ If this button is pressed the connected input image is saved in the file specified in the file path given in File Name. The Info field shows whether the store operation was successful or if any error occurred.
Info¶
-
name:info, type:String¶ This is a read-only status field showing information and error information, normally about the recent store operation.
File Name¶
-
name:unresolvedFileName, type:String, deprecated name:path¶ This is the file name parameter which normally should contain the full absolute path to a file with an extension specifying the file format to use.
Note that also variables can be used such as $(NETWORK), $(HOME), and $(DemoDataPath) to specify paths into the current network directory, the user’s home direcory and to the installed example data directory of MeVisLab.