MERIT¶
- MLModule¶
genre
authors
Tobias Boehler,Doerte van Straaten,Jan Strehlow,Stefan Wirtzpackage
dll
definition
keywords
Purpose¶
The module MERIT encapsulates the MEVIS Image Registration Toolkit, a framework for the implementation and usage of image registration methods. By default, it allows the computation of an affine-linear image registration. A template image T (also called moving image or source image) is transformed to improve the spatial alignment between T and a reference image R (also called fixed image or target image). In addition, the MERIT module allows the dynamic extension of the standard linear image registration using a plug-in interface.

Usage¶
Connect the two images, choose appropriate parameters (see details below) and press the Automatic Registration button to start the registration. Alternatively you can can run a defined number of registration steps (Multiple Steps) or do a single iteration (Single Step). Various parametric settings can be adjusted in the corresponding tabs.
Details¶
MERIT has a lot of features, see the parameter section to learn about all of them:
Automatic registration using an affine-linear transformation (or translation, rigid, similarity, or rigid+scale only).
Multi-resolution methods using image pyramids with adjustable pyramid scales, stop levels and number of levels.
Nearest neighbor, cubic, Lanczos and linear image interpolation methods, separately selectable for internal and output interpolations.
Transformation in world coordinate system, considering image orientation and patient coordinate system.
Customizable transformation order. Individual transformations can be switched off completely.
SSD, NCC, LCC, NMI and NGF similarity measures.
Support of 3-D and 2-D registration methods.
Readily extendable source code structuring, featuring a UML-modeled class hierarchy following the traditional registration paradigm, extendable base classes for registration, transformation, similarity measure, etc., which can be assessed through corresponding C++ headers, as well as image classes, image interpolation methods, etc., are re-usable in customized registration components.
Single and multiple iterations to be able to explore the registration progress in detail.
Multi-threading support using OpenMP processor threads.
Plugin support via base field input and existing exemplary plugin algorithms using the plugin-framework.(see MERITPluginsNonLinear: non-linear registration using gaussian/elastic filtering, volume-preservation, SSD/LCC/NGF image similarities).
Newton-type optimizer for the linear registration, with step size control using linear line search or Armijo’s rule.
Convergence criteria, e.g. Gill-Murray-Wright, for a unified convergence behavior of all applied registration algorithms.
Curve outputs to display multi-resolution error decrease and other values, with selectable curves (relative/absolute error, etc.).
Non-linear deformation field output in order to display vector fields or grids.
Validity checks for connected image inputs to ensure stable computational behavior.
Mask image input to compute similarities/derivatives on image subsets only.
Initialization routines to automatically center input images (e.g., for multi-modal image fusion).
Delayed load of input images to avoid costly internal updates.
See the publication on MERIT for further information: Boehler, T.; van Straaten, D.; Wirtz, S.; Peitgen, H.O (2011): A robust and extendible framework for medical image registration focused on rapid clinical application deployment. In: Computers in Biology and Medicine 41, pages 340-349. DOI: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2011.03.011.
Interaction¶
No special interactions than parameter settings are possible.
Tips¶
Tips and Tricks:
Make sure to select the appropriate dimensionality (2-D/3-D) before starting the registration.
To inspect the current deformation on each level with the reference image, compare the warped image to the corresponding scaled reference and template image from the first and second image output.
Turn off
Resample z\-axisfor images with substantially fewer slices than in-plane resolution.Choosing the desired number of levels explicitly can be sometime advantageous. If required, set the
Stop Levelto 0 to perform iterations on the finest level.Experiment with the
Scale Factor, sometimes factors not equal to 0.5 produce better results, as more information is considered per voxel.Non-overlapping images can be pre-aligned, have a look at the initialization routines.
The Newton optimizer with Armijo’s line search is a good choice for affine-linear transformations.
Trace the error reduction by inspecting the output curves, as these illustrate the performance on each level.
Known Bugs:
Hopefully none.
Windows¶
Default Panel¶
The automatic panel contains five tabs, which summarize different aspects of the parameterization of MERIT.
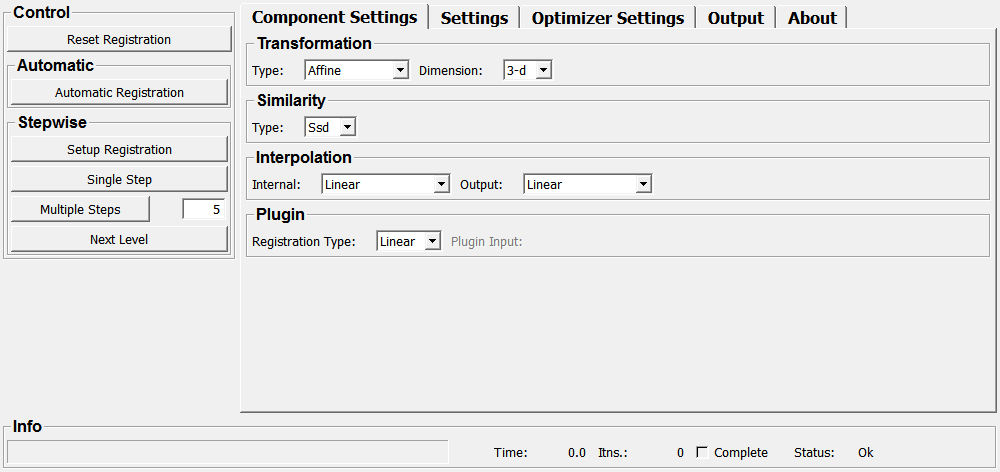
In the first tab, all components for registration following the standard registration scheme, can be chosen. This the transformation type, the similarity measure, the interpolation type and whether a plugin should be used or not.
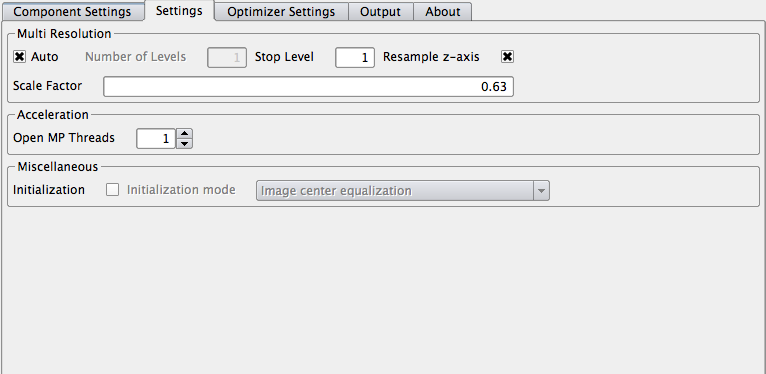
In the settings tab, all parameters for Multi-Resolution, Hardware-Acceleration and Initialization can be set.
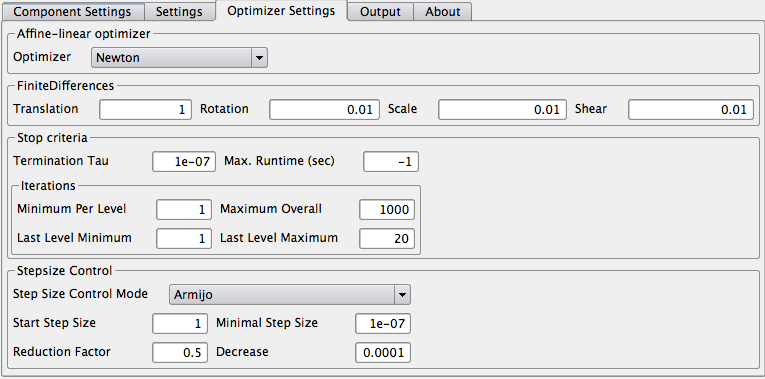
The optimizer-settings-tab contains all parameters regarding the optimizer, the discretization and the step size control mechanism.
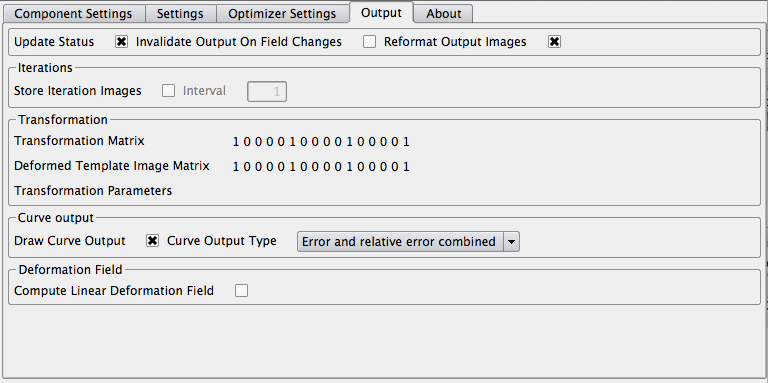
In the output-tab all settings regarding the output (transformation and image) can be set.
The last tab gives some informations about MERIT, contacts and the current version.
Input Fields¶
MERIT has four image inputs and one base input. The first two input images are mandatory while the other are optional.
input0¶
- name: input0, type: Image¶
Reference image R. It stays fixed during registration.
input1¶
- name: input1, type: Image¶
Template image T. It will be transformed during registration.
input2¶
- name: input2, type: Image¶
Optional mask image. It can be used to specify the regions where similarity is evaluated. The mask image needs to have the same size as the reference image. The similarity will be computed using only non-zero masked voxels. Voxels masked with zero do not contribute to the registration.
input3¶
- name: input3, type: Image¶
Optional initial deformation field (in same size as the reference image). The field is only evaluated during non-linear registration.
registrationPlugin¶
- name: registrationPlugin, type: MLBase¶
This input field can be used to connect a MERIT plugin. You can connect your own image registration module (it does not matter whether it is rigid or non-rigid) here, and make use of MERIT’s components like reformatting, similarity measures, image stacks, etc. Generally, MERIT plugins are provided by other modules via base outputs. The MERIT framework provides an easy-to-use extension mechanism for these plugins. More details will be added.
Output Fields¶
MERIT has five output fields. The first three outputs give the reference, template and warped template image, respectively. Furthermore, deformation fields (if switched on) and error plots (if switched on) are accessible via the last two output fields.
output0¶
- name: output0, type: Image¶
Reference image.
output1¶
- name: output1, type: Image¶
Template image.
output2¶
- name: output2, type: Image¶
Warped template image, i.e. the template image on which the transformation was applied. The transformed template image generally resides in the reference domain.
output3¶
- name: output3, type: Image¶
Deformation field. For each voxel a vec3 is generated which describes the backward-mapping voxel-coordinate displacement of this voxel. The resulting deformation can be visualized for instance using the modules
SoView2DVectorFieldVieworSoView2DDeformationGridView.
outputCurve¶
- name: outputCurve, type: MLBase¶
It displays error values vs. number of iterations (relative or absolute errors).
Parameter Fields¶
Field Index¶
Visible Fields¶
Reset Registration¶
- name: reset, type: Trigger¶
Resets the registration.
Single Step¶
- name: iterateOnce, type: Trigger¶
Starts a single iteration, and continues the active registration.
Multiple Steps¶
- name: iterateNumberOfTimes, type: Trigger¶
Computes a defined number of iterations, and continues the active registration.
Iterate Number Of Times Number¶
- name: iterateNumberOfTimesNumber, type: Integer, default: 5¶
Declares the number of iterations that are calculated when pressing
Multiple Steps.
Automatic Registration¶
- name: iterateAutomatically, type: Trigger¶
Starts the automatic registration. The algorithm stops when the termination criteria hold.
Stop Level¶
- name: iterateAutomaticallyStopLevel, type: Integer, default: 1¶
Lowest level of the image stack for which a registration is computed. Level 0 means full image resolution, levels higher than 0 indicate that the registration will finish at this particular level. The computation of the registration on the lowest level may take a while, especially for substantially large images. If larger than 0, the final transformation result will be interpolated appropriately.
Maximum Overall¶
- name: iterateAutomaticallyMaximumNumberOfIterations, type: Integer, default: 1000, minimum: 1¶
Maximum number of iterations that are calculated on each level if termination criteria do not hold before. This parameter is only evaluated when
Automatic Registrationis selected.
Last Level Maximum¶
- name: iterateAutomaticallyMaximumNumberOfLastLevelIterations, type: Integer, default: 20, minimum: 1¶
Maximum number of iterations that are calculated on the last level if termination criteria do not hold before. This parameter is only used when
Automatic Registrationis selected. Typically, the maximum number of iterations on the last level is smaller or equal to the number of iterations on the other levels, avoiding large computational costs.
Minimum Per Level¶
- name: iterateAutomaticallyMinimumNumberOfLevelIterations, type: Integer, default: 1, minimum: 1¶
Minimum number of iterations that are calculated on each level. This number is superior to termination criteria which might already want to finish registration. Sometimes it is advantageous to perform at least 2-4 iterations per level. This parameter is only used when
Automatic Registrationis selected.
Last Level Minimum¶
- name: iterateAutomaticallyMinimumNumberOfLastLevelIterations, type: Integer, default: 1, minimum: 1¶
Minimum number of iterations that are calculated on the last level. This number is superior to termination criteria which might already want to finish registration. Sometimes it is advantageous to perform at least 2-4 iterations on the last level. This parameter is only used when
Automatic Registrationis selected.
Termination Tau¶
- name: iterateAutomaticallyTau, type: Double, default: 1e-07¶
Termination criteria precision. See parameter tau in termination criteria of Gill, Murray and Wright ( Gill, Murray, Wright: Practical Optimization, Elsevier Academic Press, section 8.2.3 Termination Criteria ). The smaller this parameter is, the stricter are the criteria, i.e. the more iterations are calculated.
Max. Runtime (sec)¶
- name: iterateAutomaticallyMaxRunTime, type: Integer, default: -1¶
Maximum runtime in seconds. This parameter is only evaluated when
Automatic Registrationis selected.
Auto¶
- name: autoCalcNumberOfLevels, type: Bool, default: TRUE¶
If set to
trueMERIT automatically computes the maximumNumber of Levelsfor the given image pair according to the usedScale Factor.
Number of Levels¶
- name: iterateAutomaticallyNumberOfLevels, type: Integer, default: 1¶
Number of levels of the image stacks MERIT generates for the multi-resolution image registration. Denotes the number of levels of the Gaussian image pyramid. MERIT automatically checks if the number of levels allows the generation of a valid multi-resolution stack.
Scale Factor¶
- name: iterateAutomaticallyScaleFactor, type: Float, default: 0.63, minimum: 0.01, maximum: 0.99¶
The images of each image stacks are downsampled using this scale factor. Use factors in the range [0,1]. MERIT automatically checks if the scale factor allows the generation of a valid multi-resolution stack.
Next Level¶
- name: registrationNextLevel, type: Trigger¶
Switch to the next level manually during stepwise registration. Used in combination with
Setup Registration,Single StepandMultiple Stepsto step through the iterations.
Step Size Control Mode¶
- name: registrationStepSizeControl, type: Enum, default: Armijo¶
The stepsize control method adapts the stepsize into the direction of descent to prevent too large or too small steps. In every iteration the algorithm generates a direction of descent to decrease the error value, as required for the internal Newton step. The stepsize control method adapts the stepsize into that direction to prevent too large or too small steps. See Nocedal, Wright: Practical optimization for details.
Values:
Title |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Armijo |
Armijo |
Compares old and new error value and decreases stepsize until new error value is considerably smaller than old error value. This also takes the gradient of the error function into account. |
Wolfe |
Wolfe |
Compares old and new error value and decreases stepsize until new error value is considerably smaller than old error value. This also takes the gradient of the error function into account and additionally sets requirements on the curvature. |
Off |
Off |
No stepsize control. A fixed stepsize is used. |
Line-search |
Line-search |
Also called progressive line search, which only searches in calculated direction and cuts the length until progress is reached. |
Start Step Size¶
- name: registrationStartStepSize, type: Float, default: 1¶
Length of step into direction of descent which is first tried in every iteration. The effective step size can be less because stepsize control methods reduce the stepsize if necessary.
Minimal Step Size¶
- name: registrationMinStepSize, type: Float, default: 1e-07¶
Minimum stepsize which is used.
Reduction Factor¶
- name: registrationStepSizeReduceFactor, type: Float, default: 0.5, minimum: 0, maximum: 1¶
If the new error value is still too high the stepsize is reduced using the stepsize reduction factor and the new error value is evaluated again.
Decrease¶
- name: registrationStepSizeSufficientDecreaseFactor, type: Float, default: 9.9999997e-05, minimum: 0, maximum: 1¶
This factor is only necessary for
Step Size Control ModeArmijo, additionally contributing to step size convergence.
Slope Decrease¶
- name: registrationSlopeSufDecreaseFac, type: Float, default: 1e-07, minimum: 0, maximum: 1¶
Sufficient decrease factor for
Step Size Control ModeWolfe.
Internal¶
- name: interpolationMode, type: Enum, default: Linear¶
Interpolation that is used during registration when transforming the template image. Generally, voxel intensities do not lie on grid points and are thus resampled using one of the strategies detailed below. Interpolation of the output image can be set separately in the field
Output.
Values:
Title |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Nearest Neighbor |
Nearest Neighbor |
Rounds the image intensity value of the warped voxel to those of the the nearest voxel value. |
Linear |
Linear |
Linearly interpolates a new voxel intensity value from its neighbor voxel intensities. |
Cubic |
Cubic |
New voxel intensity value is calculated from its neighbor voxel intensities using cubic spline interpolation. |
Lanczos |
Lanczos |
New voxel intensity value is calculated from its neighbor voxel intensities using Lanczos interpolation. |
Type (transformationMode)¶
- name: transformationMode, type: Enum, default: Affine¶
Type of linear transformation used for the registration.
Values:
Title |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Translation |
Translation |
Transformation includes only translation, i.e. three degrees-of-freedom (in 3-D) are optimized. |
Rigid |
Rigid |
Transformation includes translation and rotation. Six degrees-of-freedom (in 3-D) are optimized. |
Similarity |
Similarity |
Transformation includes translation, rotation and one scale parameter which is equal in all three dimensions. Seven degrees-of-freedom (in 3-D) are optimized. |
Rigid + Scale |
Rigid + Scale |
Transformation includes translation, rotation and scaling. Nine degrees-of-freedom (in 3-D) are optimized. |
Affine |
Affine |
Transformation includes translation, rotation, scaling and shearing. Twelve degrees-of-freedom (in 3-D) are optimized. |
Transformation Matrix¶
- name: transformationMatrix, type: Matrix, default: 1 0 0 0, 0 1 0 0, 0 0 1 0, 0 0 0 1¶
4x4 homogeneous matrix which describes the affine-linear transformation.
Deformed Template Image Matrix¶
- name: deformedTemplateImageMatrix, type: Matrix, default: 1 0 0 0, 0 1 0 0, 0 0 1 0, 0 0 0 1¶
4x4 homogeneous matrix which codes the affine-linear transformation directly to the world matrix of the template image. You can set the new world matrix of the transformed template image directly using an
ImagePropertyConvertmodule.
Type (similarityMeasureMode)¶
- name: similarityMeasureMode, type: Enum, default: SSD¶
The similarity measure S evaluates the similarity of the reference image R and the template image T. MERIT minimizes the error E ( R, T ) = 1 - S ( R, T ) to spatially align the images R and T .
Values:
Title |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Ssd |
SSD |
Sum of Squared Differences error measure, in particular suitable for images with a close intensity relationship, e.g., mono-modal registration. |
Ncc |
NCC |
Normalized Cross Correlation similarity measure, considers intra- and inter-class variances of both images, based on Pearson’s correlation coefficient. Allows the registration of images with a linear intensity-relationship, e.g., inverted images. |
Lcc |
LCC |
Local Cross Correlation similarity measure. Evaluates the local cross-correlation coefficient in a local 3x3x3 window around each voxel. LCC has properties related to NMI (see below) and is robust to non-linear intensity relations. |
Nmi |
NMI |
Normalized Mutual Information similarity measure, maximizes the joint Shannon entropy values of both images, based on histogram analysis. Probably the most robust and standard similarity measure for multi-modal intensity-based image registration. |
Ngf |
NGF |
Normalized Gradient Field similarity measure. A rather new similarity measure which considers the sum of angles of all image gradient vectors. Since only derivatives contribute to this computation, even multi-modal images can be registered. |
NMI Bins¶
- name: similarityMutualInformationBinSizeNumber, type: Integer, default: 32, minimum: 1, maximum: 4096¶
Number of gray value histogram bins for NMI calculation. This parameter is only necessary in case the similarity measure
Typeis set to NMI. NMI is calculated using gray value histograms. Therefore gray values of the images are merged into equally distributed bins. This means the larger the number of bins, the finer the “resolution” of the histogram and the more gray value levels are distinguished.
Translation¶
- name: registrationFiniteDifferencesTranslation, type: Float, default: 1, minimum: 0¶
Sets the displacement in millimeters to approximate similarity measure derivatives based on the central difference quotient.
Rotation¶
- name: registrationFiniteDifferencesRotation, type: Float, default: 0.0099999998, minimum: 0, maximum: 3.1495¶
Sets the displacement in radians to approximate similarity measure derivatives based on the central difference quotient.
Scale¶
- name: registrationFiniteDifferencesScale, type: Float, default: 0.0099999998, minimum: 0, maximum: 1¶
Sets the displacement in relative scale factors to approximate similarity measure derivatives based on the central difference quotient.
Shear¶
- name: registrationFiniteDifferencesShear, type: Float, default: 0.0099999998, minimum: 0, maximum: 1¶
Sets the displacement in shear factors to approximate similarity measure derivatives based on the central difference quotient.
Registration Type¶
- name: registrationType, type: Enum, default: Linear¶
Switch between linear registration and plugin registration.
Values:
Title |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Linear |
Linear |
Standard internal MERIT affine-linear registration. |
Plugin |
Plugin |
Plugin registration. |
Plugin Input¶
- name: registrationPluginName, type: String¶
Name of the plugin registration detected at the plugin input.
Curve Output Type¶
- name: curveOutputTypes, type: Enum, default: Error and relative error combined¶
Describes which error plots are displayed. A good way to visualize error plots is using the modules
SoDiagram2Dwith legend switched on,StylePaletteandSoExaminerVieweras shown in the example network.
Values:
Title |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Error only |
Error only |
Plots iteration number vs. absolute error value. |
Relative error only |
Relative error only |
Plots iteration number vs. relative error value. Reference value is the error value on the specific level before start of the registration. |
Error and relative error combined |
Error and relative error combined |
Plots iteration number vs. absolute and relative error values. |
Combined errors overview mode |
Combined errors overview mode |
Plots iteration number vs. error value and relative error value. On every level, the value of 1.0 is added to the relative error value. |
Draw curve output¶
- name: drawCurveOutput, type: Bool, default: TRUE¶
States if error plots should be generated.
Output¶
- name: outputInterpolationMode, type: Enum, default: Linear¶
Interpolation used for the output images. Interpolation used during the registration process is set separately using
Internal.
Values:
Title |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Nearest Neighbor |
Nearest Neighbor |
Rounds the image intensity value of the warped voxel to those of the the nearest voxel value. |
Linear |
Linear |
Linearly interpolates a new voxel intensity value from its neighbor voxel intensities. |
Cubic |
Cubic |
New voxel intensity value is computed via cubic spline interpolation from its neighbor voxel intensities. |
Lanczos |
Lanczos |
New voxel intensity value is computed via cubic spline interpolation from its neighbor voxel intensities. |
Resample z-axis¶
- name: isZAxisResampling, type: Bool, default: TRUE¶
States if the images are resampled in z-dimension when the image stacks are generated.
Dimension¶
- name: registrationDimensionType, type: Enum, default: 3-D¶
Specifies the image dimension (2-D or 3-D).
Values:
Title |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
3-d |
3-D |
3-D registration. |
2-d |
2-D |
2-D registration. |
Open MP Threads¶
- name: openMPNumberOfThreads, type: Integer, default: 4, minimum: 1¶
Number of threads used for the calculation. It will be automatically adjusted when MERIT is instantiated, but can be set to a lower value if desired.
Time¶
- name: registrationTimeRequired, type: Float, default: 0¶
States the time the registration required to finish.
Itns.¶
- name: registrationNumberOfIterationsRequired, type: Integer, default: 0¶
Overall number of iterations the registration required to finish.
Complete¶
- name: isRegistrationCompleted, type: Bool, default: FALSE¶
States if the registration has finished.
Update status¶
- name: isUpdateCurrentStatus, type: Bool, default: TRUE¶
States if the current progress, e.g. the progress bar, is updated in every iteration.
Compute linear deformation field¶
- name: isComputeLinearDeformationField, type: Bool, default: FALSE¶
States if a deformation field is computed for linear registration. Note that the deformation is always in the voxel-coordinate system.
Setup Registration¶
- name: init, type: Trigger¶
Prepares the registration. This field is required only for stepwise registration. It loads images, creates image stacks, performs initialization (if switched on) and calculates initial error values.
Initialization Mode¶
- name: initMode, type: Enum, default: Image center equalization¶
Different types of initialization to automatically center input images before actual image registration. E.g. for multi-modal image fusion or follow-up analysis.
Values:
Title |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Off |
Off |
No initialization. |
Image center equalization |
Image center equalization |
Template image center is transformed onto reference image center. |
Center of gravity equalization |
Center of gravity equalization |
Template center of gravity is transformed onto reference center of gravity. |
Binary center of gravity equalization |
Binary center of gravity equalization |
Experimental: Template center of gravity is transformed onto reference center of gravity. Image gray value are not weighted during center of gravity calculation, but contribute if larger than minimum gray value and do not contribute if equal to minimum value (to distinguish background and object). |
Center equalization and translation |
Center equalization and translation |
Template image center is transformed onto reference image center. Additionally the template image is translated coarsely in all three image dimensions (see field |
Center of Gravity equalization and translation |
Center of Gravity equalization and translation |
Template center of gravity is transformed onto reference center of gravity. Additionally the template image is translated coarsely in all three image dimensions (see field |
Input Matrix |
Input Matrix |
An arbitrary |
Initialization¶
- name: isInitPositioning, type: Bool, default: FALSE¶
If set to
trueinitialization is performed.
External Initialization Matrix¶
- name: inputInitMatrix, type: Matrix, default: 1 0 0 0, 0 1 0 0, 0 0 1 0, 0 0 0 1¶
Input matrix used for initialization if
Initialization Modeis set to Input Matrix.
Invalidate output on field changes¶
- name: isInvalidateFields, type: Bool, default: FALSE¶
If set to
trueoutput fields are invalidated on field changes.
Reformat output images¶
- name: isReformatOutputImages, type: Bool, default: TRUE¶
If true the deformed template image output is actually reformatted, else only the new world matrix is set.
Version¶
- name: meritVersionInfo, type: String, persistent: no¶
MERIT version info.
Transformation Parameters¶
- name: linearTransformationParameters, type: String¶
Affine-linear transformation parameters (3x translation, 3x rotation, 3x scaling, 3x shear).
Store iteration images¶
- name: isStoreTimeStep, type: Bool, default: FALSE¶
Activate storage of images for each iteration.
Interval¶
- name: storeTimeStepsIntervalSize, type: Integer, default: 1, minimum: 1¶
The interval for which an image will be stored.
Optimizer¶
- name: registrationOptimizationMethod, type: Enum, default: Newton¶
Optimizer method for the built-in affine-linear registration.
Values:
Title |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Approx. Newton (diag(H)) |
Approx. Newton (diag(H)) |
Approximated Newton, using diagonal entries of Hessian only. This is faster but not as accurate. |
Newton |
Newton |
Newton optimizer. |
Status¶
- name: statusCode, type: Enum, persistent: no¶
The Status field reflects the internal state of the module.
Values:
Title |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Ok |
OK |
Status OK, everything can be handled. |
Invalid Input |
INVALID_INPUT |
At least one of the module inputs is invalid. |
Invalid Parameter |
INVALID_PARAMETER |
At least one parameter of the registration settings is set incorrectly (e.g. 2D-Mode activated and 3D-images at input or vice versa). |
Out Of Memory |
OUT_OF_MEMORY |
There is not enough memory to create all necessary image stacks. |
Unknown Error |
UNKNOWN_ERROR |
All other errors. |
commentString¶
Hidden comment field enabling the reporting of comments. Useful in some tests.