VideoLoad¶
- MLModule¶
author
package
dll
definition
see also
keywords
Purpose¶
The VideoLoad module provides basic access to video files. The access is generally limited to files/codecs supported by the backend that is used for your operating system (see Details section). Furthermore this module only supports video files with 1 or 3 color channels of 8 bit depth.
The single frames of the video are loaded into the Z-, T- or U-dimension, as selected by the user.
Usage¶
Select a video file in the field “Video File”. Per default “Auto Load” is activated and the frames are written to the Z-dimension, so usually you are done by selecting the file.
Check the “Status” field for errors, if it states “File open” you should be able to see your video on output0.
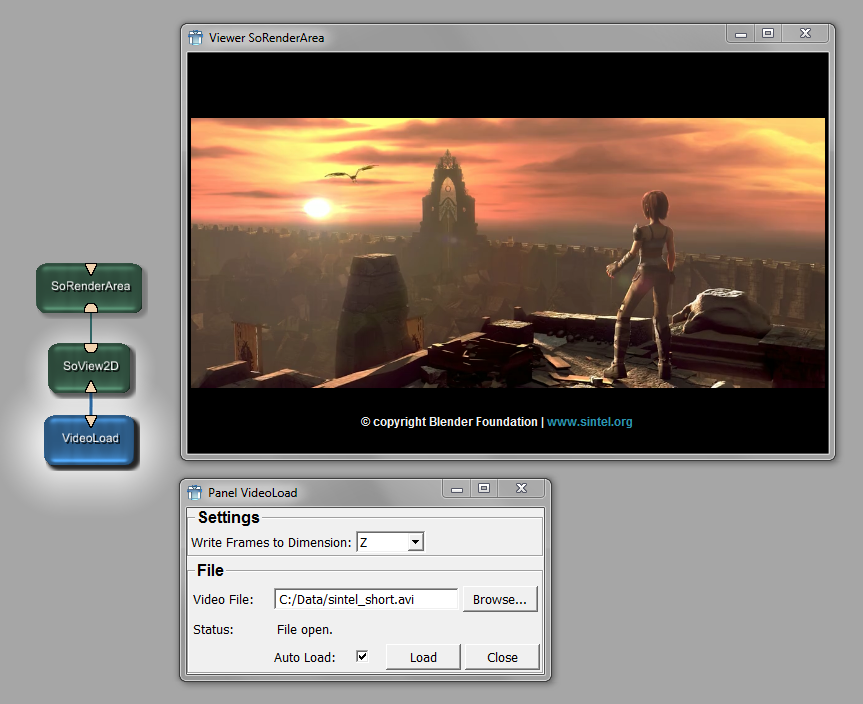
Details¶
The VideoLoad module uses the VideoCapture functionality of OpenCV which provides a very basic access to video files. OpenCV again uses different backends to access video files on different systems:
Windows: Currently OpenCV uses the outdated VfW API (Video for Windows) instead of DirectShow. This means that only a very limited amount of formats/codecs is supported. Therfore you might need to re-encode a video to a supported format. We hope OpenCV will switch to DirectShow soon …
macOS: OpenCV uses the Quicktime/AVFoundation API, all codecs available to Quicktime will be supported.
Linux: OpenCV uses the FFMPEG library, which supports many formats/codecs.
Tips¶
A video format that is supported on all plattfroms is the I420 format. You can use the open source tool “mencoder” of the MPlayer project to convert a video to the I420 format with the following command: mencoder in.avi -ovc raw -vf format=i420 -o out.avi
Output Fields¶
output0¶
- name: output0, type: Image¶
The video.
Parameter Fields¶
Field Index¶
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Visible Fields¶
Update¶
- name: update, type: Trigger, deprecated name: load¶
Press to load the file manually.
Clear¶
- name: clear, type: Trigger, deprecated name: close¶
Press to close the file manually.
On Input Change Behavior¶
- name: onInputChangeBehavior, type: Enum, default: Clear, deprecated name: autoLoad,shouldAutoUpdate,shouldUpdateAutomatically¶
If activated, attempts to load files automatically if the “Video File”-field changes.
Values:
Title |
Name |
Deprecated Name |
|---|---|---|
Update |
Update |
TRUE |
Clear |
Clear |
FALSE |
Status Code¶
- name: statusCode, type: Enum, persistent: no¶
Reflects module’s status (successful or failed computations) as one of some predefined enumeration values.
Values:
Title |
Name |
|---|---|
Ok |
Ok |
Invalid input object |
Invalid input object |
Invalid input parameter |
Invalid input parameter |
Internal error |
Internal error |
Status Message¶
- name: statusMessage, type: String, persistent: no, deprecated name: status¶
Show the status of the file, wich can be:
“File not open” = File wasn’t attempted to be opened yet.
“File open” = File was sucessfully opened.
an error message = Well, something went wrong …
Has Valid Output¶
- name: hasValidOutput, type: Bool, persistent: no¶
Indicates validity of output field values (success of computation).
[]¶
- name: updateDone, type: Trigger, persistent: no¶
Notifies that an update was performed (Check status interface fields to identify success or failure).
In Video File¶
- name: inVideoFile, type: String, deprecated name: videoFile¶
Specifies the video file to be opened.
Write Frames to Dimension¶
- name: inFrameDimension, type: String, default: Z, deprecated name: frameDimension¶
Specifies to which dimension the frames should be written. Default is Z.
Maximum Frames to Sweep¶
- name: inMaxFramesSweep, type: Integer, default: 50, minimum: 0¶
The OpenCV VideoCapture class is used to extract the frames. Tis class provides the possibility to set the extracted frame index, which invokes a seek operation, which is optimized e.g. in ffmpeg. However, the seek operation is slow compared to simply extract the next frame. Hence, the user can provide the maximum difference between a required frame and current frame for which the seek operation will be avoided.
Out Frame Rate¶
- name: outFrameRate, type: Double, persistent: no¶
Frame rate of the video [frames/sec]
Out Codec¶
- name: outCodec, type: String, persistent: no¶
Codec of the video